今天來認識 Cog 的好夥伴 ── Extension。
進度
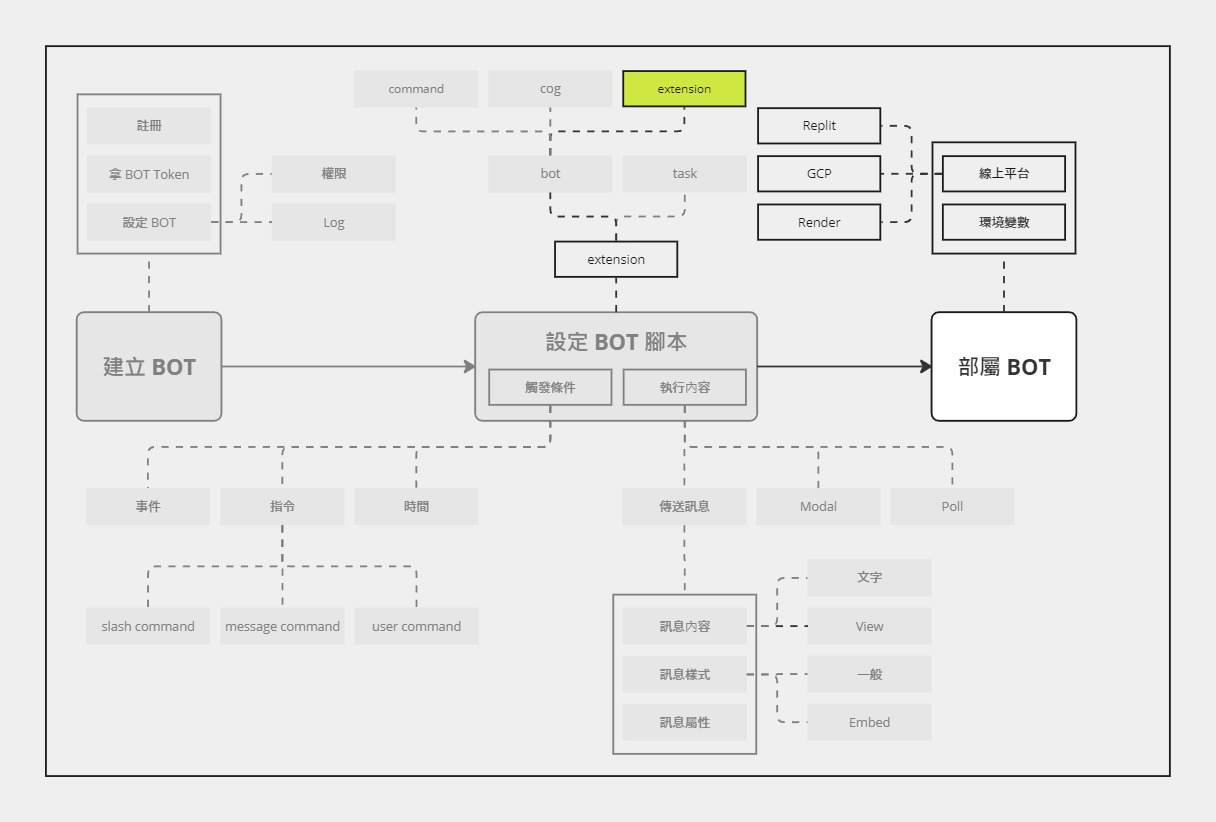
Extension 是與 Cog 不同的另一種指令管理做法,同樣可以做到拆分檔案的效果。而且,更厲害的是,Extension 還有 hot-reloading 的功能,在實際應用時更廣泛。
雖然通常 Extension 會與 Cog 搭配使用,但其實就算沒有 Cog,Extension 也可以獨立運作。
Extension Extension 本質就是 .py 檔,但一定要有一個 coroutine 的 setup 函數作為進入點 (entry point),並且這個函數只能有一個參數 bot。
Extension 架構 在看範例之前,先來看一下 Extension 架構
1 2 3 4 5 6 from discord.ext import commandsasync def setup (bot: commands.Bot ): bot.add_command(hello)
或是結合 Cog (這是比較常見的用法)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 from discord.ext import commandsclass MyCog (commands.Cog): def __init__ (self, bot: commands.Bot ): self.bot = bot async def setup (bot: commands.Bot ): await bot.add_cog(MyCog(bot))
如同前面所述,最關鍵的就是 setup 函數,至於裡面到底要直接用 add_command 還是用 add_cog 都可以。
第一個 Extension 這個範例的架構有點像昨天的 Cog 的範例。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @commands.command() async def hello (ctx: commands.Context ): await ctx.send(f'Hello {ctx.author.display_name} .' ) async def setup (bot: commands.Bot ): await bot.add_command(hello)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 import discordfrom discord.ext import commandsintents = discord.Intents.default() intents.message_content = True bot = commands.Bot(command_prefix='' , intents=intents) @bot.command() async def load (ctx: commands.Context ): await bot.load_extension("utils.hello" ) await ctx.send("hello extension loaded" , ephemeral=True ) @bot.command() async def reload (ctx: commands.Context ): await bot.reload_extension("utils.hello" ) await ctx.send("hello extension reloaded" , ephemeral=True ) @bot.command() async def unload (ctx: commands.Context ): await bot.unload_extension("utils.hello" ) await ctx.send("hello extension unloaded" , ephemeral=True ) @bot.event async def on_command_error (ctx: commands.Context, error: commands.CommandError ): await ctx.send(f"發生錯誤了: {error} " ) bot.run('token' )
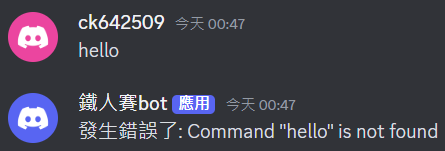
執行後,如果直接輸入 hello,會觸發 CommandNotFound 的錯誤。
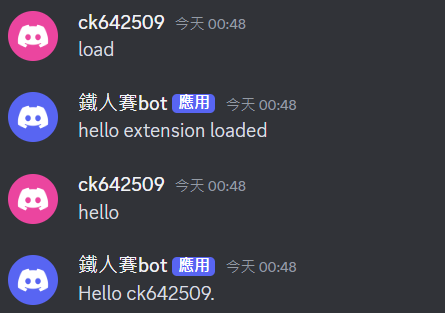
但是,如果輸入 load,就可以使用 hello 了。
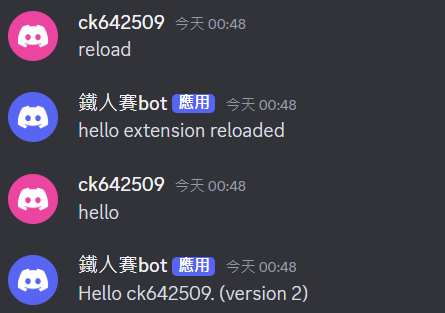
此時,如果去修改 utils/hello.py 內的訊息,接著輸入 reload (不必重啟主程式),可以發現訊息發生變化了!這就是所謂的「hot-reloading」!
1 2 3 @commands.command() async def hello (ctx ): await ctx.send(f'Hello {ctx.author.display_name} . (version 2)' )
最後,如果再輸入 unload,就又回到無法使用 hello 的狀態。
發生了什麼事? 有了昨天 Cog 的經驗,這次應該很好理解。重點有三個:
load 觸發的 load_extensionreload 觸發的 reload_extensionunload 觸發的 unload_extension
相較於 Cog,Extension 這三個函數的參數格式比較統一,都是 Extension 的名稱,格式為字串 (str)。
Extension 名稱基本上就是 .py 檔的檔名。名稱的規則與 Python 的套件一樣:
不用加 .py
如果是在某個資料夾內,就用 . 隔開。(例如:在 utils 資料夾內的 hello.py,就要用 utils.hello)
如果不喜歡這麼「絕對路徑」的寫法,也可以換個比較「相對路徑」的寫法:
1 2 3 4 @bot.command() async def load (ctx: commands.Context ): await bot.load_extension(".hello" , package="utils" ) await ctx.send("hello extension loaded" , ephemeral=True )
Extension 的更多應用 既然 Extension 使用的是檔案名稱,那麼其實就可以利用 os.listdir 去取得所有檔案名稱並一次性全部載入,不需要去管到底檔案名稱是什麼。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @bot.command() async def load (ctx: commands.Context ): for filename in os.listdir("./ext" ): if filename.endswith(".py" ): await bot.load_extension(f"ext.{filename[:-3 ]} " ) await ctx.send(f"{filename[:-3 ]} loaded" , ephemeral=True )
小結 今天介紹了 Extension 的用法,包含建立、載入、更新、移除。明天會開始介紹如何部屬 Discord BOT!